15 Nutrients that Protect the Brain from Dementia

Nutrients that protect the brain come from specific foods and supplements. Reduce your chances of getting dementia or some other neurological disorder by making your diet the MedDiet, and taking supplements as well.
Nutrients that protect the brain is the topic of an important new study published in the Journal of Preventive Medicine and Hygiene entitled Dietary supplements in neurological diseases and brain aging evaluates 15 over-the-counter supplements that can help reduce the chances of suffering from some form of dementia as you get older. As you’ll soon see, the researchers did a thorough job of reviewing the scientific literature to find the 15, but as they underscore, the right diet is essential.
Neurodegenerative diseases like dementia and Alzheimer’s are of multifactorial origin, and result in progressive loss of neuronal function in the brain, leading to cognitive impairment and motor neuron disorders.
This is a big problem for many of us. Dementia impacts approximately 6.5 million Americans — and those numbers are predicted to go up. The CDC estimates that by 2060, 14 million Americans may be diagnosed with Alzheimer’s, the most common form of dementia. Worldwide, says the World Health Organization. As the proportion of older people in the population is increasing in nearly every country, this number is expected to rise to 78 million in 2030 and 139 million in 2050
There’s a way to improve your odds of keeping your brain intact, and the primary thing you need to do for that is to evaluate what you put in your mouth, both food and supplements.
Let’s first look at food.
Food-derived Nutrients that Protect the Brain
The researchers in the Preventative Medicine study reviewed several clinical studies demonstrating the effect of Mediterranean Diet (MedDiet) on neurodegenerative progression, such as those found in dementia and Alzhiemer’s. These studies cite the MedDiet as being the best brain-protective diet.
Yep, the Blue Zoners strike again!
As you would expect, a healthy diet shapes a healthy mind. Diet quality has:
- A strong association with brain health,
- Influences the onset and consequences of neurological diseases, and
- May influence mental health at the individual and population level.
There’s a two-way link between diet and brain health
As another recent study — this one published in JAMA Neurology entitled Association Between Consumption of Ultraprocessed Foods and Cognitive Decline — underscores, the link between an unhealthy diet, impaired cognitive function and neurodegenerative diseases is made evident by examining the brain health of those consuming ultra-processed food.
Researchers in the JAMA study examined 10,775 individuals over ten years, and found that those who consumed over 20% or more of their calories from ultra-processed foods had a higher risk of dementia. In a 2000-calorie diet, this equates to only 400 calories each day coming from ultra-processed foods. That’s about 20 potato chips or 30 French fries. Yep, it doesn’t take much of such “foods” to fog the brain.
The good news is that a diet like the MedDiet links to the opposite result: Adopting a healthy diet, along with specific supplement-derived nutrients could ultimately afford prevention and management of neurological diseases and brain aging.
Given the importance of diet in neurological diseases management (as well as everything else in the body), the Preventative Medicine study focuses on the dietary components, natural compounds and medicinal plants that have proven beneficial in neurological diseases and for brain health.
And it all begins with the MedDiet.
The MedDiet possesses food-derived nutrients that protect the brain. These nutrients promote antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immune, neuroprotective, antidepressant, anti-stress and senolytic responses. These play an essential role in the prevention and management of neurological diseases and inhibit cognitive decline in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and Huntington’s diseases.
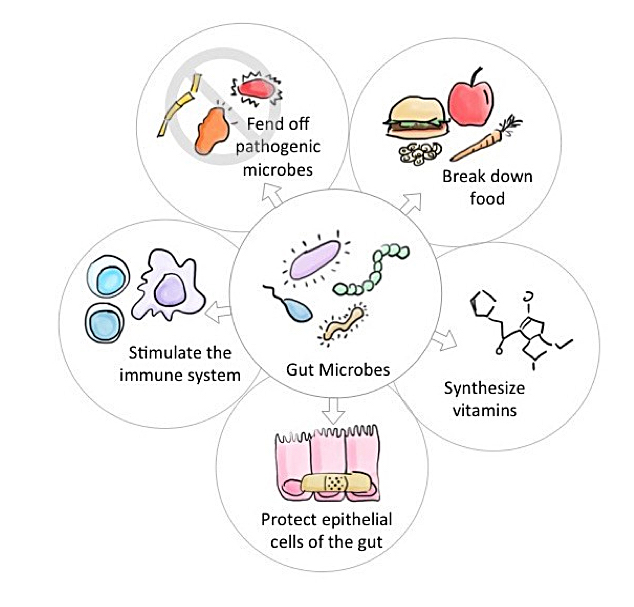
The MedDiet also modulates the gut-brain axis by promoting and nourishing a diversity of gut microbiota
Your gut microbes influence nearly every aspect of your health. The “good” bugs help make and keep you healthy, but to flourish they require fiber and the polyphenols abundant in plant food. The “bad” bugs will make you sick; to flourish they require the saturated fats and sugar abundant in processed foods.
Read: Test Your Gut Health — Here’s How
Several studies also reviewed by the Preventive Medicine study show that the MedDiet can alleviate depression
Depression, the foremost cause of disability, is increasingly thought to be a subtle neurological disorder — and the MedDiet is a good choice for improving overall mental health and relieving stress and anxiety.
Research-based evidence suggests that dietary measures can be an adjunctive treatment for mental disorders. The MedDiet is rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, healthy fats and proteins that are high in polyphenols.
As many as 37 studies have reported a reduction in symptoms of depression in groups of persons on diets rich in polyphenols. An observational study also revealed that following the MedDiet was pivotal for reducing depressive outcomes in overweight patients with metabolic syndrome.
A study led by Roberto Vicinanza, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Gerontology at the University of Southern California, reported a positive impact of the MedDiet on mental health in elderly patients with multimorbidity. They also observed that the diet prevented symptoms of depression in these patients, resulting in healthy aging.
In view of the importance of diet in neurological diseases management, the Preventive Medicine study focuses on the dietary components, natural compounds and medicinal plants that have proven beneficial in neurological diseases and for brain health. Among them, polyphenols, omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins and several ayurvedic herbs have promising beneficial effects.
Let’s now take a look at these recommended supplement-derived nutrients that are deemed to protect the brain.
Supplement-derived Nutrients that Protect the Brain
The Preventive Medicine study reviews 15 supplement-derived nutrients that protect the brain from neurological damage:
- N-acetylcysteine (NAC)
- Phospholipids
- Phosphatidylcholine
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA
- Melatonin
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Neurotropic B vitamins
- S-adenosyl methionine (SAMe)
- Tryptophan
- Magnesium
- Polyphenols
- Bacopa monnieri
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)
- Vacha (Acorus calamus)
- St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum)
I’ll briefly cover each in the table below. If interested, you can learn more about them in the study.
Supplement-derived Supplements
(Go to the Preventative Medicine study for more details)
| Supplement | What It Is | What It Does |
| N-acetylcysteine (NAC) | A compound derived from the amino acid L-cysteine. | Can alleviate stress and mediate the impacts of toxicity, infections and inflammatory conditions by supporting the body’s antioxidant and nitric oxide systems. Is a precursor to glutathione, the body’s “Master Antioxidant”. |
| Phospholipids | A lipid containing a phosphate group in its molecule, e.g., lecithin. | A brain-specific nutrient thought to decrease in the brain with aging, leading to cognitive decline and impairment as well as lower PKC activity. May prove beneficial in correcting disrupted neural function. |
| Phosphatidylcholine | The major phospholipid component of cell membranes. | Replenishes age-induced reductions in the hippocampus and frontal cortex of elderly persons (89-92 years). |
| GABA | A non-protein amino acid found in high concentrations in different parts of the brain. | It’s the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the human cerebral cortex, and has demonstrated effects on several neurological disorders. |
| Melatonin | A neurohormone (produced by nerve cells and secreted into the circulation) secreted by the pineal gland in the brain. | Melatonin affects the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, reproductive system and metabolism, and regulates body weight. Acting as a chronobiotic, melatonin modifies the phase and amplitude of biological rhythms. |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | A type of polyunsaturated fatty acids | Essential for a variety of physiological functions involved in neuroinflammation, neurotransmission and neurogenesis; therefore, play a major role in brain development, performance and aging. A deficiency leads to many neurological conditions such as depression, ADHD, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, dementia and autism. |
| Neurotropic B vitamins | Vitamins B1, B6 and B12. | Have crucial roles in the nervous system. Their deficiency leads to various neurological disorders. Synergistic interaction of B1, B6 and B12 may improve neuropathic pain, motor control and nociception (pain signaling). |
| SAMe | A major methyl donor that influences central nervous system function via cell transmethylation pathways, including but not limited to DNA methylation. (Methyl is a small molecule made of one carbon and three hydrogen atoms. Methyl groups are added or removed from proteins or nucleic acids and may change the way these molecules act in the body.) | It’s a strong antidepressant with impacts in mouse models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease. SAMe supplementation alters brain bioenergetics and is an effective treatment for depression. |
| Tryptophan (TRP) | An essential amino acid. | Is involved in various physiological processes including immunity, neuronal function and gut homeostasis. Gut microbiota produce specific TRP metabolites that indirectly influence host physiology. An alteration in TRP metabolites results in neurological and psychiatric disorders. |
| Magnesium | An important mineral for homeostasis in the human body | Plays an essential role in neuroprotection, neuromuscular conduction and nerve transmission. It is a mineral of intense interest due to its capacity to protect the nervous system against ecotoxicity, thus improving many neurological disorders. |
| Polyphenols | Are important nutrients abundant in spices and foods. | Have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and senolytic activities; they modulate the gut microbiome and promote protein aggregation and stability. Show promise for preventing neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Bacopa monnieri | An Indian ayurvedic medicinal plant. | Treats various neurological disorders, enhances digestion and improves learning, cognitive function and concentration. Helps restore cognitive deficit and enhances mental and brain function. Promotes repair of damaged neurons, neuronal synthesis and synaptic activity. |
| Ashwagandha | An Indian medicinal plant thought to promote long life, youthful vigor and intellectual capacity. | Used in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, general frailty, nervous exhaustion and insomnia. It has anti-inflammatory, anti-tumour, antioxidant, immunomodulatory and anti-neuropsychiatric effects. |
| Vacha | Indian ayurvedic medicinal plant. | Used to treat insomnia, melancholy, memory loss, hysteria, depression, mental disorders; neurological, gastrointestinal, kidney, respiratory, liver, and metabolic disorders. |
| St. John’s wart | A perennial plant with yellow flowers that has been used in traditional European medicine as far back as the ancient Greeks. | Used to treat anxiety and mild to moderate depression, and neurological disorders. |
Given the size of this list of brain-protecting supplements, a reasonable question is which to prioritize? Well, the study that covered them did not rank their efficacy; however, it did present details about various studies indicating the neurological benefits derived from the supplements, as well as some dosage details, which are important:
“… their [the supplements] effects are dose-dependent and must be administered in a precise manner.”
I suggest that if any of the supplements interest you, go to the study and look at the further details offered there. Whether or not you decide if any of these supplements are for you, do shift your diet to the MedDiet — you can’t supplement your way to good mental health.
For more details about the MedDiet, read my post, The Blue Zone Diet Will Transform You.
Your Takeaway
Oxidative stress and neuroinflammation are key factors in the onset and progression of neurodegenerative diseases, such as dementia and Alzheimer’s. A diet rich in biologically active compounds with antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties, such as MedDiet, affords significant neuroprotection.
Several natural compounds, minerals and medicinal plants have also been tested in clinical trials and animal studies and some, such as phospholipids, GABA, NAC, omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, curcumin*, resveratrol*, St. John’s wort, Vacha and Bacopa monnieri have proven beneficial, safe and economical in the treatment of NDs. However, their effects are dose-dependent and must be administered in a precise manner. These potentially beneficial dietary components need to be evaluated in large clinical trials to assess their wider application across patients of different ethnic origin.
(* Interestingly, curcumin and resveratrol were not covered in the Preventative Medicine study except for the mention in the Conclusion, but I have you covered: Check out more about curcumin here, and more about resveratrol here.)
Last Updated on December 29, 2022 by Joe Garma