3 GLP-1 Weight Loss Supplements for Lower Blood Sugar and Better Health
GLP-1 weight loss is something new to most people. A recent study showed that a drug called semaglutide stimulates this naturally produced hormone. And the results are outstanding.
Stimulating GLP-1 weight loss supplements took on new importance based on a just-released study that showed that the drug semaglutide promoted significant weight loss in obese participants.
We’re talking up to 20% of body weight, so this has fostered a lot of attention.
Semaglutide is a drug that requires a doctor’s prescription and will cost users about $1,000 per month out-of-pocket, given that health insurance companies will not subsidize weight loss drugs.
This is unfortunate, because not only can semaglutide help reduce significant weight loss in those suffering from obesity, but also reduces the elevation of blood sugar in response to carbohydrate consumption, thereby improving health outcomes not only for type 2 diabetics, but for prediabetics as well.
This post reviews the potential weight loss and general health improvement effects of the hormone that Semaglutide stimulates — GLP-1 — and reveals the three over-the-counter supplements available to you now that may provide similar benefits.
I’ll begin by summarizing the semaglutide study, explain what GLP-1 is and does, detail the importance of blood sugar control for healthy aging, and present the foods and three supplements that can boost GLP-1:
- The semaglutide study results –up to 20% of body weight loss
- GLP-1 weight loss and insulin management
- Fasting blood sugar (above 85 mg/dL = age-related disease)
- 3 supplements to stimulate GLP-1 weight loss
The Semaglutide Study Results — As Much As 20% Loss In Body Weight
As Gina Kolata of the New York Times put it:
For the first time, a drug has been shown so effective against obesity that patients may dodge many of its worst consequences, including diabetes…
She was referring to semaglutide, a drug made by Novo Nordisk, that has been marketed as a treatment for Type 2 diabetes. But now there’s a twist. In a clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers at Northwestern University in Chicago found that semaglutide is an anti-obesity medication.
The study had just under 2,000 participants at 129 centers in 16 countries inject themselves weekly with semaglutide or a placebo for 68 weeks. Those who used semaglutide lost an average of 14.9% of their body weight compared with 2.4% among those who used the placebo. More than a third of the participants on semaglutide lost more than 20% of their body weight. Moreover, symptoms of diabetes and pre-diabetes improved in many patients.
Such impressive results begs the question, What in the heck is semaglutide?
Semaglutide is an analogue of the naturally occurring hormone, GLP-1. In this context, an “analogue” is a compound that is structurally similar to another or performs the same functions. Because the drug semaglutide is an analogue of GLP-1, it can have some of the same effects of this naturally-occurring hormone, including having an impact on body weight and blood sugar.
Semaglutide is a synthetic version of a GLP-1 that acts on appetite centers in the brain and in the gut, producing feelings of satiety.
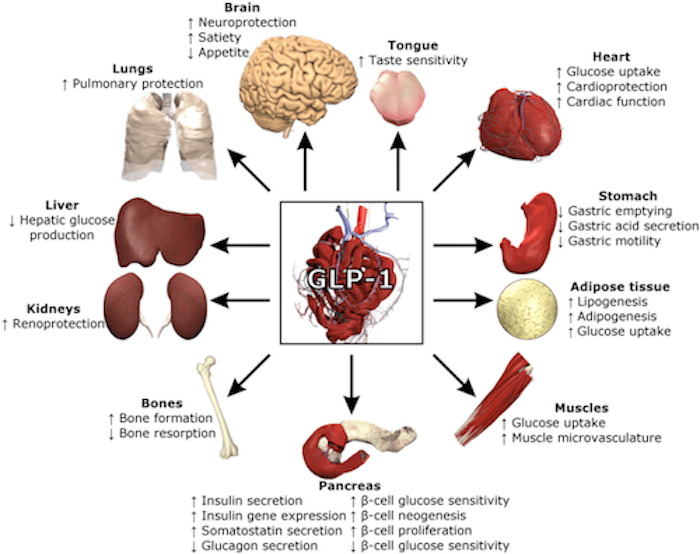
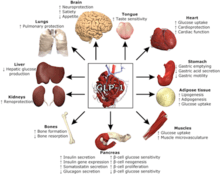
GLP-1 Weight Loss and Insulin Management
Simply put, GLP-1 (glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide) is a hormone (specifically, an incretin) that is naturally activated after delivery of nutrients to the gastrointestinal tract subsequent to food ingestion.
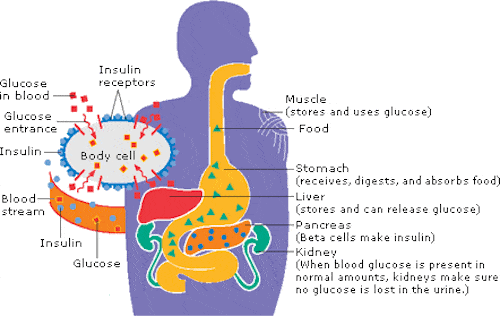
Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas that regulates the amount of glucose in the blood. Insulin helps your body turn blood sugar (glucose) into energy. It also helps your body store it in your muscles, fat cells, and liver to use later, when your body needs it. After you eat, your blood sugar (glucose) rises. This rise in glucose triggers your pancreas to release insulin into the bloodstream. The lack of insulin can cause diabetes.
Incretins, like GLP-1, are a group of metabolic hormones that stimulate a decrease in blood glucose levels. Incretins are released after eating and augment the secretion of insulin released from the pancreas. Some incretins like GLP-1 also inhibit glucagon release, and slow the rate of absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream.
Slow glucose (sugar) absorption into your bloodstream is desired so that the pancreas does not have to produce a lot of insulin. If your body can achieve this, you’re ‘insulin sensitive”; meaning, you don’t need to make much insulin to control blood glucose levels.
Insulin is needed to shuttle glucose from your blood into your muscle and fat cells where it can be used for energy or stored for later use. Without insulin, your blood glucose levels would stay elevated for a much longer period. High, sustained blood sugar is a condition that can lead to surprisingly negative health conditions.
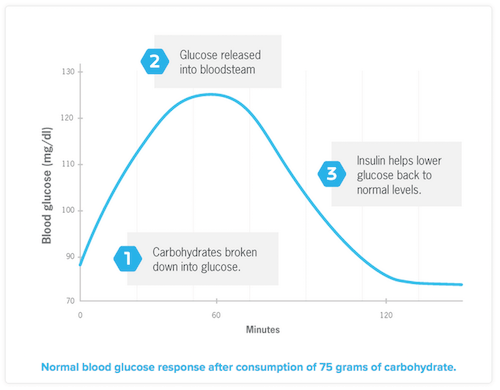
The objective is to produce the minimum amount of insulin to reduce (flatten) the spike indicated at #2 in the graph below.
Fasting Blood Glucose Above 85 mg/dL Promotes Diseases of Aging
A worthwhile read is the February 2012 Life Extension Magazine article, Suppress After-Meal Blood Sugar Surges. It makes the following research-backed claims:
- Excess blood sugar has become the norm: In addition to the 26 million Americans with diabetes, the Centers for Disease Control estimate that more than a third of the general population is now pre-diabetic.
- Data confirm that risk for most degenerative diseases and death rise dramatically when fasting blood glucose exceeds 85 mg/dL.
- After-meal glucose “spikes” inflict silent damage to cells via multiple mechanisms and have been linked to cardiovascular disease, cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, kidney failure, and retinal damage.
- The prediabetic fasting glucose range of 100 to 125 mg/dL is much too high. Optimal fasting glucose should be within the range of 70 to a maximum of 85 mg/dL.
Over the years, the Life Extension Foundation has thoroughly surveyed the scientific literature about the impact of high blood sugar on aging and the chronic illnesses associated with aging. Their assessment is that maturing individuals with blood sugar levels above 85 mg/dL are at substantially increased risk of virtually all degenerative diseases, including:
- Cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Kidney disease
- Pancreatic dysfunction
- Diabetic retinopathy (which can lead to blindness)
- Neuropathy (nerve pain and dysfunction)
I confess that I have a hard time keeping my fasting blood glucose at 85 mg/dL, despite nearly never eating processed/fast food or foods with high natural or added sugar, as discussed in You Absolutely Need To Lower Your Blood Sugar, Part 2 — The 10 Step Solution. What I do to maintain the fasting blood glucose target of 85 mg/dL is to cycle in and out of the various supplements outlined in the “10 Step Solution” article.
3 Supplements To Stimulate GLP-1 Weight Loss
Before I get to supplements, know that none will ever supplant a consistently nutritious diet.
A 2016 study published in the journal Nutrition & Metabolism laid out the best food choices to support GLP-1 activation that could lead to desired insulin sensitivity for blood glucose control and weight loss, which include:
- Mediterranean Diet rich in organic cold pressed, virgin olive oil
- High fiber foods
- Oatmeal
- Nuts
- Lean protein
If you don’t eat those foods regularly, consider supplementation.
These three supplements can help activate GLP-1:
- Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens M and Lactobacillus kefiri K
- L-arginine
- Glutamine
Let’s take a quick look at each.
(1) Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens M and Lactobacillus kefiri K
These are two probiotics that are a bit hard to find, but find them I did in Garden of Life Raw Probiotics.
As detailed in this 2015 study (abstract only), Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens M and Lactobacillus kefiri K have GLP-1 stimulating capabilities.
(2) L-arginine
The journal Obesity published a 2018 paper that showed the amino acid L-arginine increases after-meal (postprandial) circulating GLP-1 in humans, and as well supports the general acceptance of the satiating effect of protein.
Amazon.com’s choice for L-arginine is the Nature’s Bounty L-Arginine brand.
(3) Glutamine
Glutamine is an important amino acid with many functions in the body, including assisting in immune function and intestinal health. A 2009 paper showed that glutamine effectively increases circulating GLP-1,and may represent a novel therapeutic approach to stimulating insulin secretion in obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Amazon.com’s choice for L-glutamine is Optimum Nutrition L-Glutamine.
Your Takeaway
The first thing I want to underscore is that there are many supplements that can effectively help you reduce fasting and postpranadial blood glucose spikes and sustained elevation. (My articles “10 Step Solution” and “4 Tricks” review several.)
The three supplements covered in this post were selected specifically due to the studies that support their potential to stimulate GLP-1 weight loss, although I’d be surprised if they would be as effective as the drug semaglutide. But, remember, to use semaglutide you need both a doctor’s prescription and about $1,000 per month.
If you’re obese or nearly so, I suggest you ask your doctor if it makes sense for your to try the three supplements above, as well as the foods mentioned.
The bottom line is that most us need to reduce our blood sugar levels if we’re to achieve long lasting health. To achieve that, get into the habit of:
- Eating fibrous foods, nuts, lean protein and fermented foods to feed your beneficial microbes, such as Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens M and Lactobacillus kefiri K.
- Move your body often and vigorously so that blood sugar can feed your muscles and provide energy for your effort, rather than circulating in your blood stream until it’s added to your fat deposits.
- Use supplements to help the cause, such as the probiotics Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens M and Lactobacillus kefiri K, the amino acids L-arginine and glutamine, and any of those listed in these blood sugar management articles.
Last Updated on April 11, 2023 by Joe Garma