Use This Salt Substitute for High Blood Pressure

The best salt substitute for high blood pressure has reduced sodium and contains potassium. A new meta study concludes that such a salt substitute can help lower hypertension, a serious chronic illness that more than one billion adults have, many of whom don’t even know it.
The best salt substitute for high blood pressure contains low sodium and some potassium, says a recently published meta study.
The rest of this post is conceived to encourage you to:
- Determine if you have high blood pressure (hypertension), and
- Do something about it.
In a future post I’m going to detail what you can to prevent heart disease, including hypertension, but right now I want to encourage you to simply assess if you’re at risk for hypertension, or have it, and if either is the case, to simply use a salt substitute for high blood pressure.
A salt substitute for high blood pressure that contains low sodium and high potassium can help lower hypertension. That’s the conclusion of a systematic review and meta analysis of the effects of salt substitutes in a recently published in the BMJ journal Heart. A team of researchers analyzed 21 trials and 31,949 participants included, 19 of which reported the effects on blood pressure and five that reported the effects on clinical outcomes.
Using a salt substitute for high blood pressure makes a lot of sense for a lot of people, given the soaring rates of hypertension worldwide.
The American Health Association reports that 121.5 million or 47% of US adults had hypertension from 2015 thru 2018. There are about 250 million adults in the U.S. You do the math — there’s an astonishingly high number of Americans suffering from high blood pressure.
Much of the rest of the world’s population is dealing with hypertension as well. The World Health Organization reports that an estimated 1.28 billion adults aged 30 to 79 years worldwide have hypertension (that’s inclusive of Americans). An estimated 46% of adults with hypertension are unaware that they have the condition.
Here's what I cover:
Ideally, this post will encourage you to find out if you have hypertension and incentivize you to take the minimum action to lower it — use a salt substitute for high blood pressure that has low sodium and high potassium content.
What is hypertension?
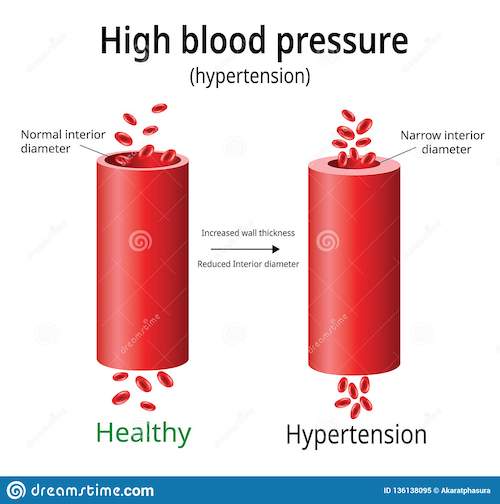
Hypertension is high blood pressure. And high blood pressure is when the body’s smaller blood vessels (the arterioles) narrow, causing the blood to exert excessive pressure against the vessel walls and forcing the heart to work harder to maintain the pressure.
It’s safe to say that hypertension is a big health problem. The Mayo Clinic says it can lead to:
- Damaged and narrowed arteries
- Aneurysm
- Coronary artery disease
- Enlarged left heart.
- Heart failure
- Stroke
- Dementia
- Cognitive issues
- Kidney issues
- Damage to the retina and optic nerve
- Sexual dysfunction
How do you know if you have hypertension?
The accurate way to find out is to measure it. The intuitive way to find out is to examine your diet and activity level. You can also look at your family history.
A diet high in salt, fat, and/or cholesterol can lead to hypertension, and result in chronic conditions such as kidney and hormone problems, diabetes, and high cholesterol. So any of that is your first clue.
But why not just measure your blood pressure with a blood pressure cuff.
This quick video shows you how to do it accurately:
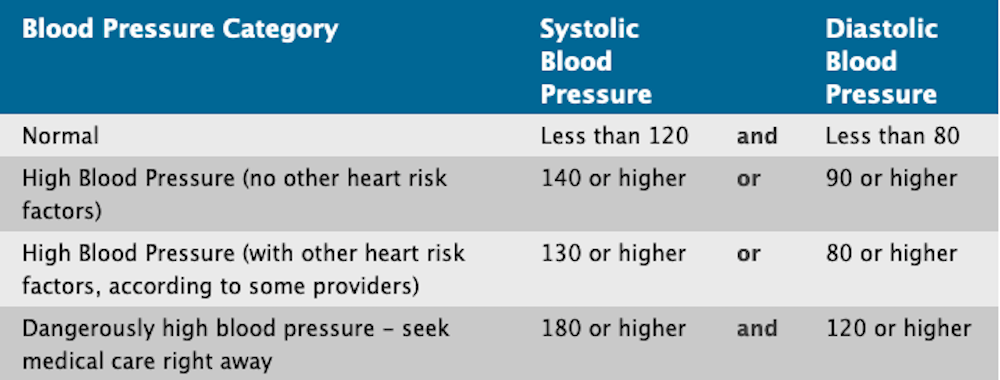
This chart from Medline shows normal to high blood pressure:
The Life Extension Foundation recommends an optimal target of 115/75 mm Hg., and suggests the risk of cardiovascular disease doubles for each increment of 20 mm Hg systolic and 10 mm Hg diastolic above 115/75 mm Hg.
This means that it’s worthwhile to get your blood pressure lower than normal, down to 115 over 75.
How do you do that?
Use a salt substitute for high blood pressure (hypertension)
As I’ve been saying, the simplest thing you can do is to use a salt substitute for high blood pressure that contains low sodium and high potassium. If you use a lot of salt, this is probably a necessary thing to do. But it’s not some cure-all for hypertention; rather a fast, doable step in the right direction.
I’m going to address at length how to reduce hypertension in a future post, but suffice to say here is that you can:
- Eat the Blue Zone diet,
- Exercise, and (once again)
- Us a salt substitute for high blood pressure that contains low sodium and some potassium. (See more options below.)
Frankly, I’m surprised that a low sodium, high potassium salt substitute is useful to lower hypertension, but that’s what the data suggests, which takes us back to that salt substiute study.
As mentioned, the study reviewed 21 other studies on the subject and concluded that:
Salt substitutes, which replace a proportion of sodium chloride (NaCl) with potassium chloride (KCl), are known to help lower blood pressure.
The study periods that were evaluated lasted from one month to five years. The proportion of sodium chloride in the salt substitutes varied from 33% to 75%; the proportion of potassium ranged from 25% to 65%.
According to the pooled data analysis:
- Salt substitutes lowered blood pressure in all the participants. The overall reduction in systolic blood pressure was 4.61 mm Hg and the overall reduction in diastolic blood pressure was 1.61 mmHg.
- Each 10% lower proportion of sodium chloride in the salt substitute was associated with an additional 1.53 mm Hg drop in systolic blood pressure and an additional 0.95 mm Hg drop in diastolic blood pressure.
- The salt substitutes lowered the risks of early death from any cause by 11%, from cardiovascular disease by 13%, and the risks of heart attack or stroke by 11%.
At this point, you may be wondering, Well, which salt substitute should I use?.
Well, the study did say that:
“Potassium- enriched salt, such as that used in the SSaSS [the study], should be considered routinely by clinicians seeking to prevent complications in patients with hypertension and by policy makers seeking to reduce the burden of blood pressure-related disease.”
But the closest it got to identifying which salt substitute they used was to say:
“Regular salt is about 100% NaCl [sodium], and salt substitute was defined on the basis of 5% or more of NaCl [sodium] being replaced with KCl [potassium chloride].”
This prompted me to scurry around to find a specific brand to tell you about. Amazon.com has a few that might fit the bill, but this one seems to clear the hurdle set by the study and is also “Amazon’s Choice”, if that’s any consolation:
Update: A Subscriber wrote to tell me about two additional salt substitutes that contain no salt, but retain its flavor, as well as a book on the topic:
NU-SALT Substitute, Sodium-free: Zero salt — Potassium chloride is the salt substitute component of the blend.
Boulder Salt Electrolyte Powder provides balanced electrolytes (that includes salt) to help ensure proper hydration during and/or after exercise. Typically, such electrolyte powders are superior to water when the exercise sessions are strenuous enough to cause profuse sweating and are of one hour or more in duration.
The High Blood Pressure Solution: A Scientifically Proven Program for Preventing Strokes and Heart Disease asserts that the majority of cases of stroke, heart attack, and hypertension can easily be prevented by maintaining the proper ratio of potassium to sodium in the die.
And that’s it for this post about a salt substitute for high blood pressure. Soon, I want to do one on a sugar substitute. Spoiler alert: I use erythritol, which has a very low glycemic index, but I haven’t done any research to see if it’s the best. Stay tuned for that by subscribing to my Newsletter.
Last Updated on February 7, 2024 by Joe Garma