New Anti-aging Research Explodes — Mitochondria, Senescence, Biomarkers and Stem Cells

New anti-aging research is continuing to increase at a prodigious pace. Brilliant researchers are choosing longevity as their specialty, and billions are getting invested in new biotech start-ups. The results are some promising new drugs under clinical trail. But in the meantime, learn what you can do now to slow your aging rate and become biologically younger.
New anti-aging research has exploded during 2020, and there’s still half the year to go. This was clearly made evident by a recent article written by Andrii Buvailo, Co-founder and Editor of BiopharmaTrend.com and staff writer Irina Bilous.
The article reviews the new anti-aging research that has recently been published. I want to summarize the article, and expand upon what you can do now to benefit from the research being conducted. (The entire article authored by Buvailo and Bilous can not be read without a site membership.)
Here's what I cover:
Let’s dig in…
Healthspan vs Lifespan
Generally speaking, the bulk of new anti-aging research that deal with longevity therapeutics does not directly target aging in a way that would stop or reverse it. Instead, these “first generation” longevity therapeutics — which include senolytics, rapamycin, mitochondrial gene therapy, and WNT pathway regulators — target chronic, age-related ailments.
The primary aim of the new anti-aging research in 2020 and prior is to slow down or reverse the progress of age-promoting biofactors, predominately those identified in the landmark paper, the Hallmarks of Aging. Many of the “hallmarks” that focus on extending human lifespan may remain beyond the reach of science for years to come, but that’s not true regarding healthspan.
Healthspan — the years a person is healthy — is largely within your control.
The distinction between lifespan and healthspan is depicted by a story that famed longevity expert Dr. David Sinclair often relates. He says he sometimes begins a lecture about longevity by asking the audience to raise their hands if they want to live to 100. A small smattering of hands rise up. Then he reframes the question by asking how many would like to live to 100 if they could maintain their current health. Most hands shoot up.
Until anti-aging research produces drugs you can access that can extend human lifespan, your focus needs to be on extending the years over which you remain healthy — healthspan, just like they do in the Blue Zones.
The relevant question then is: How can new anti-aging research help me lengthen my healthspan?.
To address that question, let’s look at the latest on research about:
- mitochondria,
- senescence,
- longevity biomarkers, and
- stem cells.
New Anti-aging Research on Mitochondrial Dysfunction
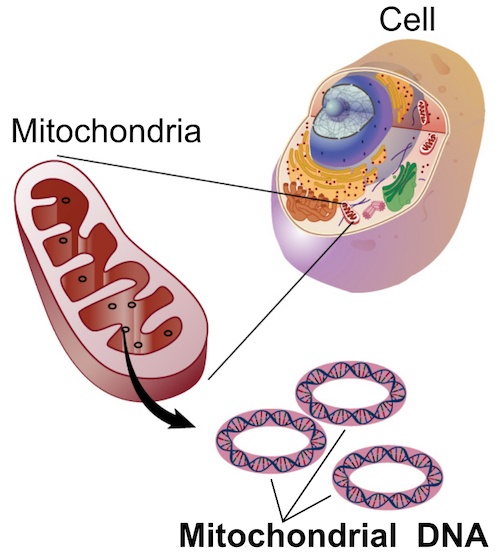
The mitochondrial theory of aging is one of the Hallmarks of Aging, and has been exhaustively studied. Mitochondria are organelles inside of cells, and are responsible for helping us convert digested food into ATP via a process called cellular respiration. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the “energy currency” that our cells use to function and keep alive, and thus keep us alive.
The process required to make this cellular energy, ATP, creates ROS (reactive oxygen species). Think of ROS as free radicals. This ROS damages the cell and mitochondrial DNA.
One of the strategies to combat mitochondrial aging is to protect mitochondrial DNA from various assaults, such as ROS damage, expressing in the nucleus. GenSight Biologics is on the cutting edge in the development of biotechnologies that can make this happen.
GenSight Biologics is working to cure Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON), which causes blindness, because this genetic disease is a good model to treat age-related loss of vision, as the common denominator between LHON and vision loss associated with aging is the loss of retinal cells.
The therapeutic approach GenSight is developing is Mitochondrial Targeting Sequence (MTS), which uses gene therapy to permit missing mitochondrial proteins to be actively shuttled into the mitochondrion, enabling the restoration of mitochondrial function necessary to effectively treat LHON. This approach disrupts the formation of damaging ROS and altered metabolism, which if left unchecked can take an accumulating toll on neurons over a period of years, including those in the retina, eventually leading to neuronal cell death.
Another example of a drug in phase III clinical trials is SkQ1, developed by Mitotech. This drug is created to treat dry eye disease by protecting the eye from oxidative stress.
Of course, mitochondria exist in nearly all of our cells, not just retinal cells, but the thinking is that MTS technology may be able to be tweaked to address various diseases that have mitochondrial dysfunction at their root, such as:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Muscular dystrophy
- Lou Gehrig’s disease
- Diabetes
- Cancer
Although there is much new anti-aging research focused on mitochondria, no magic pill or therapy will be soon available. So, what do you do in the meantime? You take matters into your own hands.
7 Ways to Bolster Your Mitochondria
The website Experience Life has an informative article about “the care and feeding of your mitochondria”. Caring for your mitochondria is one of the best ways to take care of your health — and enjoy better energy, metabolism, and mental focus in the process.
- Do strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT). Both can increase the number, and improve the function, of your mitochondria. The better your muscle mass and cardiovascular conditioning, the better your mitochondria will fare, and the more powerfully they will perform. I’ve written quite a bit about HIIT — see here.
- Avoid or eliminate ingredients that are toxic to your mitochondria, including processed flours, all sugars and refined sweeteners, trans fats, gluten, and dairy products.
- Eat six to nine cups of fresh vegetables and fruits daily. Terry Wahls, MD, recommends a variety of greens (broccoli, bok choy, etc.), brightly colored vegetables (beets, carrots, etc.), and the sulfur-rich veggies (cauliflower, cabbage, etc.) that help your body produce glutathione, a master antioxidant. She recommends blending several of your mitochondrial-building veggies and fruits in a daily smoothie.
- Dine on fiber-rich foods to help detox the poisons that can build up when mitochondria slow down. Check out my posts, A High-Fiber Diet + 8 Easy Fat-Busting Tips You Can Do Now and Eat Fiber, Live Longer, Healthier too!.
- Up your omega-3 fat intake to help build your mitochondrial membranes. Avocados, nuts, and seeds are also rich in fatty acids. Taking a fish-oil supplement is a good idea for most people.
- Brew up bone broth. When mitochondria are compromised, there is increased risk for autoimmune diseases, such as arthritis, which are caused, in part, by a leaky gut. Wahls says bone broth is rich in glutamine and other amino acids that are especially good for healing a leaky gut as well as other ailments. “It’s the secret to that old-fashioned chicken soup remedy,” she notes, “as long as you cook that soup broth with the chicken bones.”
- Take mitochondria-protective and energy-boosting micronutrients, such as Acetyl-L-carnitine, alpha-lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10, N-acetylcysteine, NADH, D-ribose, resveratrol, and magnesium aspartate. You can find all of these on Amazon.com. Sort by most popular to get an idea of, well, which brands people like.
New Anti-aging Research on Senescence
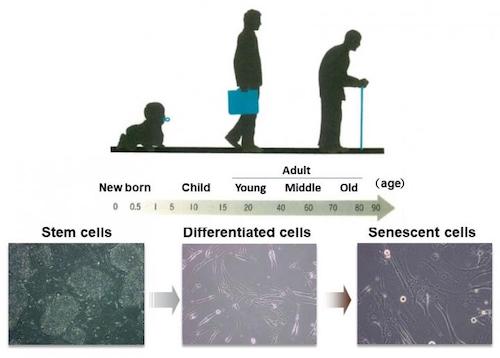
Credit: Professor Mitsuyoshi Nakao. The human body and the cells that make it up have a “program” for aging. It is thought that there is an accumulation of senescent cells in tissues and organs as we get older.
One of the reasons for many dysfunctions connected to age-related diseases is that cells go zombie on us. A “zombie” is something that’s neither dead nor alive, and so it is with cells.
Zombie cells are senescent; they can no longer reproduce or function, but they remain metabolically active. Senescent cells also damage healthy cells in their vicinity by releasing harmful molecules, many of which are inflammatory, that can harm healthy cells around them and may even induce other cells to become senescent.
The older we get, the more senescent cells we have, and that’s why cellular senescence is another Hallmark of Aging.
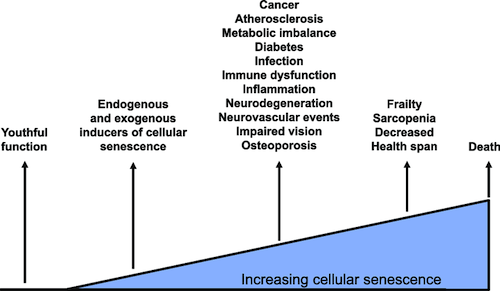
The accumulation of senescent cells with aging in multiple tissues leads to a number of age-related diseases. Targeting these cells holds the prospect of simultaneously preventing or ameliorating these age-associated morbidities.
A number of biotech startups have recently emerged that are tackling senescence, including Unity Therapeutics, backed by Jeff Bezos among other investors. The first drug Unity created to remove senescent cells failed to reduce osteoarthritis pain. (Such drugs are called senolytics.) But now Unity has another promising candidate in the pipeline called UBX1325 that targets proteins in the Bcl-xL pathway, which senescent cells rely on to survive.
Another way to get rid of senescent cells is to develop therapeutic antibodies as senolytics; they have an advantageous ability to target senescent cells without harming healthy ones. A company that leverages this approach is Veraxa, a startup from Heidelberg.
Again, like with keeping or attaining mitochondrial health, you need not wait until some senolytic drug becomes available. As I wrote in my post, Can New Senolytics Drugs Delay Aging? Part 2: Three Senolytic Drugs Available Now, three over-the-counter compounds — fisetin, quercetin and piperlonguminine, — have been studied and shown to be effective at removing some senescent cells. I take all three, even though the reputable Dr. Brad Stanfield stopped taking fisetin, citing recent research that calls into question its effectiveness.
New Anti-aging Research on Longevity Biomarkers
We all know people who look young or old for their age, and maybe they are. When I last took a biological age test using nine blood tests as biomarkers, my biological age was estimated to be about 19 years younger than my calendar years.
Such tests are important. The ability to reliably measure biological age of organs, tissues, and ultimately the whole body is needed in order to assess if any aging intervention improves biological age.
The most accurate of these bioage tests are epigenetic tests, because they are able to estimate how various lifestyle factors affect gene expression, which is the basic focus of the science of epigenetics. Turns out that although your genes are fixed (the genome), how they express (the epigenome) are not fixed — they are influenced by your behavior and environment.
Multiple data types can be used to predict age and associate the prediction with mortality, disease, general wellbeing, or other biological processes including methylation (an epigenetic test technique), biochemical parameters of the blood, gene expression (another epigenetic technique), microbiome, imaging data, and others.
As Buvailo and Bilous wrote:
“Currently, more than a dozen types of ‘aging clocks’ exist, with some of them exploiting methylation profile data, such as Horvath’s clocks and Hannum’s age predictor. Recent advances have been made by Deep Longevity, which developed what they claim to be the most accurate epigenetic clocks for today — DeepMAge. The company also released a new achievement — psychological aging clocks, both technologies are powered by deep learning-based algorithms developed by the company. Whereas with epigenetic clocks they manage to create algorithms superior to its analogs, psychological clocks will allow uncovering the aspect of aging that previously was largely understudied.
“…Hong Kong-based Deep Longevity announced that the company had been granted a patent issued by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) covering the applications of microflora profiles in the anti-aging industry: “Aging markers of human microbiome and microbiomic aging clock”. This landmark invention was originally published in Cell as a research article: “Human Gut Microbiome Aging Clock Based on Taxonomic Profiling and Deep Learning” in 2020. This article described a neural network that can estimate the age of a person based on their gut flora composition.”
You can read more about how what you do affects your healthspan, if not your lifespan, by reading my post, Why Do Twins Grow Apart? Epigenetics Tells the Tale. At the bottom of this post, I list resources that detail the specific behaviors that can make you biologically younger.
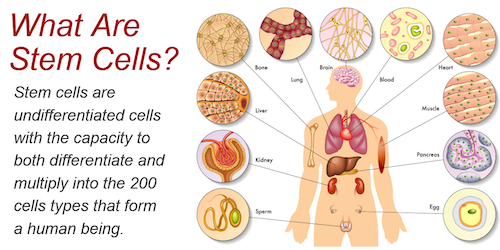
Stem Cells and Aging Research
I left stem cell research for last, because there’s little you can do right now to use the new anti-aging research on stem cells to enhance longevity or even healthspan. So, although it may be interesting to learn what new anti-aging research is being conducted in the world of stem cells, don’t hold your breath for an easy, proven and inexpensive technique to turn some of your cells into stem cells.
Why would you want to?
Well, perhaps because stem cells are the building blocks of the human body. At the start of life, they divide over and over again to create a full person from an embryo. As we age, they replenish cells in our blood, bone, skin and organs, and, theoretically, when that happens, youth happens.
A company called Biosplice (formerly Samumed) is among the few with anti-aging drugs in Phase III clinical trials. Their treatment approach is designed to force stem cells (through WNT pathway) to perform as they usually do in healthy conditions regardless where they are in the body.
The most advanced program in Biosplice’s pipeline is for cartilage regeneration and osteoarthritis treatment. Osteoarthritis is an age-related disease, as well as many others, caused by deterioration and malfunctioning of molecular pathways and tissue degeneration. But, again, although a stem cell therapy probably would be superior, if you are ailing from osteoarthritis you might check out Glucosamine sulfate.
According to the Mayo Clinic, glucosamine sulfate might provide some pain relief for people with osteoarthritis. The supplement appears to be safe and might be a helpful option for people who can’t take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
In the domain of age-related stem cell reprogramming is a company called Agex Therapeutics. In 2021, they published a paper where they were able to reprogram centenarian cells of a 114 year-old woman to pluripotency. Pluripotency describes the ability of a cell to develop into the three primary germ cell layers of the early embryo and therefore into all cells of the adult body, but not extra-embryonic tissues such as the placenta.
Agex Therapeutics has a preclinical pipeline that consists of cell-based therapeutic candidates to cope with cardiac ischemia and age-related metabolic disorders, and drug-based candidates to restore regenerative potential of aged tissues afflicted with degenerative disease.
Scholar Rock is also about to enter phase III clinical trials with the drug for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). The drug is targeted to block one of the myostatin forms (growth factor from TGF-beta family) which is expected to increase muscle mass. The previous trials confirmed the specificity of the drug to the latent myostatin, but not its receptor or active form, which should reduce the number of possible side effects from the treatment.
Your Takeaway
Given that the hot, relatively new anti-aging market could surpass $271 billion by 2024, you can expect to continue to hear about new drugs in the pipeline in the years ahead as biotechnology companies get funded and compete to discover cures for many of the Hallmarks of Aging and chronic disease states that underlie, or accelerate, the aging process.
My advice is not to passively wait for some miracle pill to save you from the ravages of aging, but rather be proactive. Genetics controls only about 20% of longevity, so a lot of how you age is within the scope of your control. This is the purview of epigenetics, and what that science tells us is that your lifestyle choices and the environment you live in matters a great deal to how well, or not, you will age.
In this post, I’ve made some suggestions about how you can begin now to slow down aging and improve your healthspan now, rather than wait for some promised pharmaceutical drug. The links below will help you get started.
- Your Anti-aging Lifestyle Must Address These Concerns
- How To Improve Your Healthspan, Say 5 Scientists
- 3 Ways to Increase DNA Methylation and Get Biologically Younger
- How 3 People Reduced Their Body Age By 29 Years In 3 Months
- How Superagers Age Superbly and Why You Can Too!
- 7 Anti-aging Interventions Backed By Science, Part 1: CR and Fasting
- Here’s How To Increase Healthspan With Exercise and Diet, Says Science.
- Why You Must Exercise for Longevity and How To Do It
- How You Can Reduce Your Biological Age By One Year Per Week
Comments? Questions? Scroll down and weigh in in the Comments section.
Last Updated on November 8, 2022 by Joe Garma