How To Strengthen Your Pancreas, Improve Digestion and Lower Blood Sugar All By Yourself
Why strengthen your pancreas? Because it produces hormones vital to your ability to digest food and assimilate carbs and fats. Moreover, about 74% of us have problems with digestion and gut health, and nearly 40% experience damaging elevated blood sugar. How about you?
Updated on August 3, 2022
To strengthen your pancreas is one of the best things you can do for a healthy, enduring endocrine system. The endocrine system is a messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system.
About a month ago, I wrote about one of the most important organs in our endocrine system, the adrenals. In that article, I showed readers how they can heal their adrenals. According to Adrenal experts Dr. Michael Lam and Dr. Josh Axe, 50 to 80% of the U.S. population have adrenal issues, which is precisely why I wrote about it – adrenal fatigue affects a lot of people and there are specific things you can do to heal them.
Today, it’s time to take a look at another very important endocrine organ, the pancreas. If your pancreas is not healthy, you could be experiencing a host of unsavory health issues that may be categorized into two buckets: digestion and blood sugar, both of which become compromised as we age.
In this article, you’ll discover:
Let’s first describe the pancreas, then get into the pancreas’ role in digestion, and finally turn to how it doles out insulin to handle blood sugar that our carbohydrate-dominate diets amp up to unsustainable and unhealthy levels.
The objective is to show you how to strengthen your pancreas to help ensure that you live a long and strong life.
Your Pancreas Is A Very Important Six Inch Powerhouse
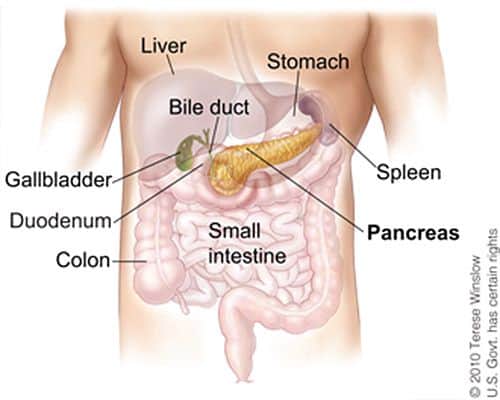
Your pancreas is a flat, oblong organ about six inches long that’s located deep in the upper left-center region of the abdomen, surrounded by the stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder and small intestine.
The pancreas has two primary functions:
- As an “Exocrine”, it produces and releases digestive fluids and pancreatic enzymes to digest protein, starch/carbs, and fat; and
- As an “Endocrine”, it produces the hormones insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin.
Yeah, exocrine vs endocrine was new to me, too. Who woulda thunk it, but the pancreas functions both as an exocrine and endocrine gland, or organ:
Exocrine glands relate to or denote glands that secrete their products through ducts opening onto an epithelium (a sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity) rather than directly into the bloodstream; whereas endocrine glands relate to or denote glands that secrete hormones or other products directly into the blood.
Functioning as an exocrine gland, the pancreas produces and excretes enzymes and digestive juices into the small intestine to break down the proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids in food after it has left the stomach. Functioning as an endocrine gland, the pancreas produces and secretes the hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate the body’s glucose or blood sugar levels throughout the day, as well as some other hormones.
As you’ll see in a moment, digestion issues may affect 74% of the U.S. population, and high blood sugar and the resulting insulin desensitivity (a bad thing) affect nearly 40% of the U.S. population. This surely means that the pancreas is a gland that we need to pay attention to if we’re to live a long and strong life.
But before we dive into those specifics, ask yourself if you may have a problem with your pancreas?
Symptoms of pancreatic problems
The symptoms of a diseased and/or problematic pancreas depend on the underlying cause, but may include:
- Pain in the upper abdomen
- Loss of appetite
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Back pain
- Bloating
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Digestive upsets
- Passing foul-smelling and fatty feces
- Consistently high blood sugar
- Obesity
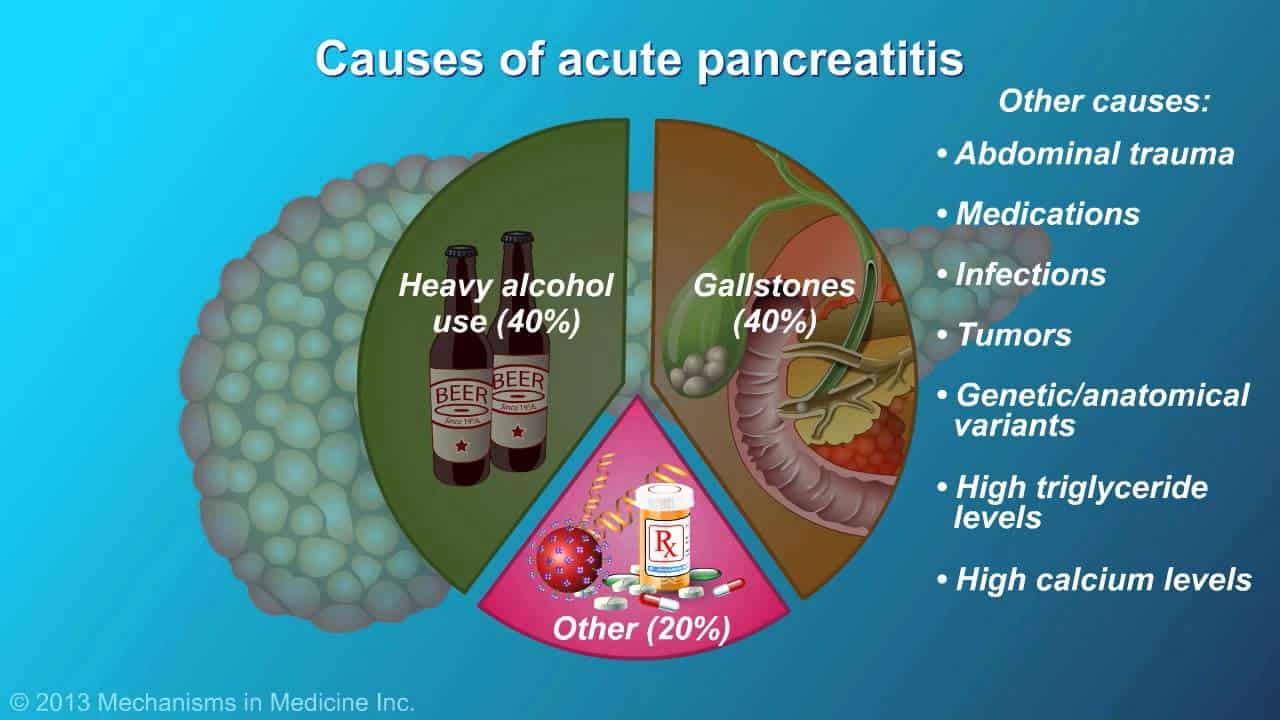
The pancreas can become impaired by several threats. It is the organ most affected by pesticides. Sugar, artificial sweeteners, and simple carbohydrates — all of which quickly spike blood sugar — also take a serious toll on the pancreas. All of these conditions are predominate in the industrialized world where its people consume too much sugar (particularly in processed food), and are affected by pesticides and other chemicals and heavy metals.
Digestion and Gut – The Pancreas’ Exocrine Function
A pancreas that is not working sufficiently in its exocrine role is referred to as “Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (“EPI”). This is a condition characterized by deficiency of the exocrine pancreatic enzymes, resulting in the inability to digest food properly, or maldigestion (a condition in which the digestive system works improperly).
The exocrine pancreas produces three main types of enzymes:
- amylase,
- protease,
- and lipase.
Under normal physiologic conditions, these enzymes (specifically, lipase) break undigested triglycerides into fatty acids and monoglycerides, which are then solubilized by bile salts.
That is if everything is working as designed. For many, perhaps most of us, it’s not.
According to a survey conducted in 2013, 74% of Americans are living with digestive symptoms like diarrhea, gas, bloating and abdominal pain, which could indicate more serious health issues.
If you think that number is rather high, it could be because AbbVie Pharmaceuticals underwrote the survey. That said it seems that the company did not begin making any digestive-related drugs till two or more years after the survey.
Let’s just say that an overlarge number of people suffer from digestive issues that compromise their health.
Commenting on the survey participants, gastroenterologist Dr. Rashini Raj said:
Over half of them never discussed it with their doctor. And that’s probably the most alarming part for me, because as you know, sometimes this can be a sign of a more serious underlying condition: celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, EPI or exocrine pancreatic insufficiency — so these are symptoms you shouldn’t ignore, and unfortunately a lot of people don’t feel comfortable talking about them.
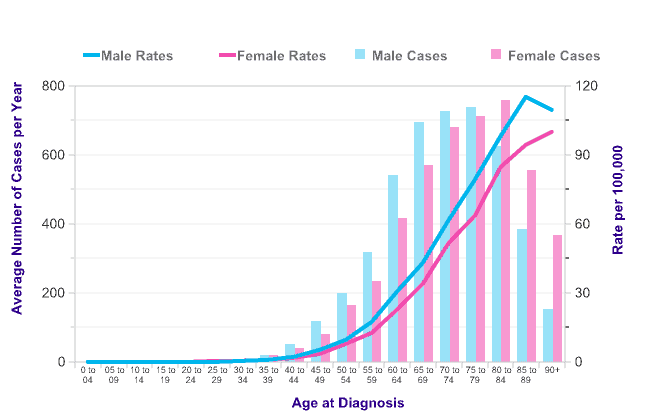
I didn’t find a graph showing the association of age with rates of EPI, but I did find one that shows pancreatic cancer diagnoses begin to dramatically increase in our forties. Given that the pancreas has to take a lot of abuse for a long time before it becomes cancerous, I think this graph is a fair warning that we need to give the pancreas some tender loving care.
According to Medscape, the diagnosis of EPI is largely clinical. It may go undetected because the signs and symptoms are similar to those of other gastrointestinal diseases, or because the signs and symptoms are not always evident. This would at least partially explain why problems with the pancreas are often not diagnosed till they produce cancer, as indicated by the above graph.
Insulin, Glucagon and Blood Sugar – The Pancreas’ Endocrine Function
As noted above, the endocrine function of the pancreas is to control blood sugar. In this day and age of sugar-laden manufactured foods and the ubiquity of processed carbohydrates – both of which spike blood sugar – that poor little six-inch gland has a lot of work to do for a lot of people.
It may not be at 74% of the population as indicated for the “digestive symptoms survey” mentioned above, but prediabetes, undiagnosed diabetes and type 2 (adult-onset) diabetes impacts many millions of us.
According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, as of 2012, 29.1 million people in the United States, or 9.3 percent of the population, have diabetes:
- 21 million people are diagnosed
- 8.1 million people with diabetes are undiagnosed (that’s 27.8%)
Thus, more than one in four people with diabetes don’t know they have the disease.
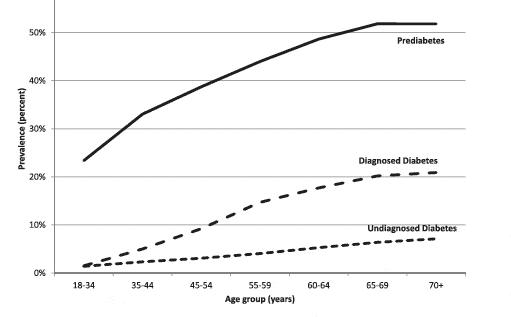
An estimated 86 million Americans aged 20 years or older have prediabetes, or “borderline” diabetes, an astounding one-quarter of the population. Add it all together — prediabetics, diabetics and undiagnosed cases — and you get:
86 + 21 + 8.1 = 115.1 million people with high blood sugar, about 37% of the U.S. population in 2012 (314.1 million)
Prevalence of Prediabetes, Diagnosed and Undiagnosed Diabetes, 2012
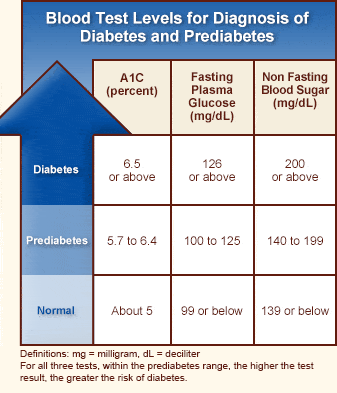
Whereas the blood sugar threshold for diabetes is 125 mg/dl or higher as measured by a fasting plasma (blood) glucose test, someone with prediabetes will test at 100 to 125 mg/dl (milligrams per deciliter). Normal blood sugar is less than 100 mg/dl. (See Life Extension’s Diabetes Management Profile Comprehensive Blood Test.)
How Insulin Works
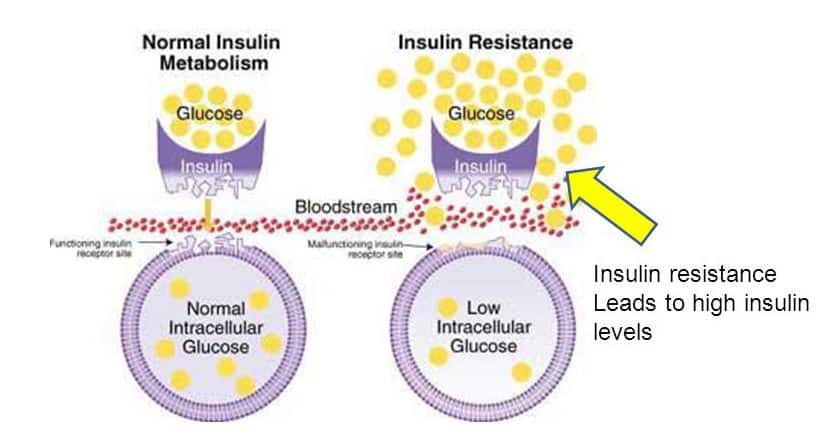
The story of blood sugar goes hand-in-glove with the story of insulin. You’re familiar with insulin, yes? It’s responsible for regulating the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats used the body for energy, and plays a critical role in balancing and maintaining healthy blood sugar (glucose) levels in the body. (Without a sufficient supply of glucose to the cells, your cells would starve and die.)
When blood glucose levels rise after a meal, the pancreas releases insulin into the blood. Insulin and glucose then travel in the blood to cells throughout the body. Insulin helps muscle, fat, and liver cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream (which lowers blood glucose levels), it stimulates the liver and muscle tissue to store excess glucose (called glycogen) and it lowers blood glucose levels by reducing glucose production in the liver.
In a healthy person, these functions allow blood glucose and insulin levels to remain in the normal range.
What happens when you’re insulin resistant is that muscle, fat, and liver cells do not respond properly to the insulin secreted by the pancreas; therefore these cells cannot easily absorb glucose from the bloodstream, resulting in a body that needs higher levels of insulin to help glucose enter cells.
The beta cells in the pancreas try to keep up with this increased demand for insulin by producing more of it. As long as the beta cells are able to produce enough insulin to overcome the insulin resistance, blood glucose levels stay in the healthy range.
The problem is that this whole process of the pancreas pumping out more insulin to handle more blood sugar over and over again eventually can lead to insulin resistance, prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. This happens because the pancreas’ beta cells fail to keep up with the body’s increased need for insulin. Without enough insulin, excess glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to prediabetes/ diabetes and other serious health disorders, such as metabolic syndrome and obesity.
A useful way to visualize insulin resistance is to use a lock and key analogy. Insulin attaches to a specific receptor on the membrane of a cell in order to allow glucose to move into the cell, like how a specific key fits in and unlocks a specific lock. When your body becomes insulin resistant, the initial amount of insulin produced by the pancreas is insufficient to open the “lock” and blood sugar increases. In response, the pancreas makes more insulin. Eventually, the system breaks down.
Lowering blood sugar isn’t the only think that the pancreas’ endocrine function does. Remember, there’s this thing called “glucagon”, another hormone that the pancreas secretes too.
Glucagon has the opposite effect of insulin on blood glucose levels. Whereas insulin lowers blood glucose levels, glucagon raises them when they become too low. It does this by signaling the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose and then release it into the bloodstream. Together, glucagon and insulin act as elements of a regulation system to keep blood sugar levels stable. Both of these pancreatic hormones are in turn regulated by somatostatin, which also plays a role in cell growth and nerve transmissions.
An important point to remember is that whenever you feel tired after eating a meal, you have eaten too many carbohydrates, which prompts insulin to be secreted from the pancreas, causing blood sugar to be converted into fats. This requires a great deal of energy, and consequently you get tired.
(See Life Extension’s Glucose Tolerance Test with Insulin (8 specimens) Blood Test)
How Well Is Your Pancreas Functioning (Know the Symptoms)?
Let’s review a host of symptoms that might indicate you’ve got a poorly functioning pancreas that you need to strengthen.
Impaired pancreatic function is implicated in indigestion, gas, constipation, heart disease, arteriosclerosis, allergies, diabetes, immune dysfunction, prostate problems, susceptibility to infection, and many other illnesses.
Sticky stool (as in it sticks to the toilet bowl) indicates a weak pancreas. Floating stool may a sign that fats in your diet are not sufficiently digested, or that the dietary fat consumed are of poor quality (trans fat, margarine, palm oil, lard).
In addition to sugar and pesticide exposure, the following factors also cause the pancreas to be stressed, impairing its function:
- Alcohol, coffee, and packaged commercial teas and juices
- Emotional stress
- Eating too fast, not chewing your food
- (Stop eating when you are no longer hungry, not when you are full.)
- Poor food combining (fruits with protein, for instance.)
- Trace mineral deficiencies (especially chromium and zinc).
- Many prescriptions and over-the-counter medications.
- Allergies — people with allergies (food and/ or environmental) have a poorly functioning pancreas, resulting in reduced production of digestive enzymes— amylase, lipase, and protease— which are needed to digest the starches, fats, and proteins that we consume.
How to Strengthen Your Pancreas and Improve Hormonal Production
Let’s say that you’re in the majority. This means that either your exocrine and/or endocrine pancreatic functions are impaired to some degree, meaning that you are experiencing symptoms of poor digestion and/or high blood sugar and the resulting insulin desensitivity.
What do you do?
The answer is that you:
- Test
- Eat differently
- Supplement
Get Tested
A very important blood test that includes Hemoglobin A1c measures your blood sugar over the past 90 days. It’s a great indicator of insulin resistance (when elevated at greater than 5.7 mg/dL).
Get this: according to Dr. Michael Galitzer, as reported in his book, Outstanding Health, when Hemoglobin A1C is very low at 5.0, there’s a 99% chance that you will be alive in ten years.
Yes, indeedy, blood sugar matters!
Two other common tests for blood sugar are Fasting Glucose and Insulin and Oral Glucose Tolerance Test.
These, and the other tests I’ve linked to in this post, are facilitated by the Life Extension Foundation (LEF), which is affiliated with the largest blood drawing centers sprinkled all over the U.S. One big benefit of using LEF is that you have access to an expert there to review your test results with you at no extra charge.
Although not ideal, you can do the fasting glucose test at home with the aid of some pretty inexpensive equipment, which I walk you through in the article, My Blood Sugar Numbers Dumbfound Me.
Eat Differently
In his aforementioned book, Outstanding Health, Dr. Glazier tells us that the pancreas functions optimally between 9:00 and 11:00 in the morning. In contrast, 12 hours later the pancreas is designed to be in rest mode and is therefore working least effectively.
Given this, Glazier makes the case that breakfast is the meal that most people are able to digest most efficiently, given the naturally occurring pancreatic enzymes prevalent in the morning. Unfortunately, he says, most Americans eat very small breakfasts, or skip breakfast altogether, and instead have their biggest meal at dinnertime, often late in the evening. It is in the evening when your pancreas is least able to produce digestive enzymes. Consequently, late-night-eating people don’t digest their food properly, go to bed with a full stomach, and then wake up feeling tired and lousy.
When the pancreas is energetically weak, all foods should be heated, very little raw foods consumed, and water should be drank at room temperature (no ice water), says Dr. Glazier.
Here’s a few important guidelines for optimal digestion that will also spare your pancreas from undue stress:
- Practice proper food combining; for instance, eat fruits by themselves and don’t combine proteins with starches.
- Avoid consuming fluids with meals, allowing one-half hour before a meal, and one hour after.
- Chew food at least 10 times per mouthful in order to optimally mix food with saliva.
- Do not eat very large meals.
- Avoid late meals and refined foods as snacks.
- Avoid excessive salt and sugar Ensure a sufficient daily intake of fiber. It is not necessary to add extra fiber if you already eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- If you are usually constipated, check with your doctor for the most appropriate fiber supplement.
- Perform physical exercise daily, on an empty stomach. Abdominal training and breathing exercises are very helpful for the digestive tract.
- Read labels carefully. The fewer the chemical names, the better.
- Avoid food coloring and unnecessary additives. The more natural, the better.
- Eat organic food, as it is free of pesticides
- Finally, make use of the drainage and detoxification techniques I share in various detoxification articles listed here to reduce your body’s burden of pesticides and other toxins.
As reported at DYI HealthRemedy, these ten foods are considered useful for healing the pancreas:
- Red grapes
- Broccoli
- Blueberries
- Cherries
- Garlic
- Reishi mushrooms
- Spinach
- Tofu (fellas, it could increase estrogen)
- Sweet potatoes
- Tomatoes
Supplement
Leptandra is an effective homeopathic remedy for the pancreas, says Dr. Glazier. According to traditional Chinese medicine, imbalances in the pancreas are linked to compulsive behavior, obsessions, and worrying. Due to the role the pancreas plays in carbohydrate metabolism, such imbalances are further linked with depression, addiction, fatigue, and hyperactivity.
Pancreatic Enzymes taken with meals can help digest the incompletely digested food that can irritate the mucous lining of the intestines, resulting in the absorption of partially digested proteins and intensifying allergic reactions. Pancreatic enzymes also play an important role in helping the immune system in its battle against infection and malignancy. Taking pancreatic enzymes on an empty stomach before you go to sleep helps to “eat up” toxic debris and waste products, allowing your liver and blood, to more easily detoxify while we are sleeping.
Pork Pancreas Enzymes are lyophilized (freeze-dried) pancreatic glandular tissue taken from organically raised pork, assuming you buy the organic version. Glandular tissues can be rich sources of nutrients, enzymes, hormone pre-cursors, and other factors that support specific gland-related metabolism and physiological function. Pork pancreas enzymes are typically potent in enzyme activities and contain high levels of amylase, protease, and lipase as well as other digestive factors naturally occurring in the pancreas.
Specific to the endocrine function of the pancreas, that dealing with insulin and blood sugar, these six supplements should be of substantial help:
Six Supplements that Support Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
| Supplement | Form | Quick Facts |
| Indian Gooseberry (Amla) | Powder or Capsule | It can work better than prescribed medicine at less cost and with no side-effects. |
| Berberine | Capsule | Studies present compelling data that show Berberine to substantially reduce blood sugar, triglycerides and cholesterol. |
| Fenugreek | Powder, Liquid, Cream or Capsule | Reduces blood sugar spikes by providing fiber and other chemicals that slow digestion. |
| Wellbetx PGX Plus Mulberry | Capsule | A specific brand consisting of a water-absorbing fiber and mulberry extract, which reduces after-meal rises in both glucose and insulin levels. |
| Chromium | Capsule | Many people are deficient of this metallic element that serves to regulate blood sugar, and help insulin transport glucose into cells where it can be used for energy. |
| Carnosine | Capsule, Lotion | One of the best “longevity supplements” with a long list of health attributes, including reducing AGEs. |
Your Takeaway On How to Strengthen Your Pancreas
Got chronic digestion issues?
Get tired after meals?
Eat a lot of carbs?
Have excess body weight?
Then get yourself tested:
- Diabetes Management Profile Comprehensive Blood Test
- Glucose Tolerance Test with Insulin (8 specimens) Blood Test
- Fasting Glucose and Insulin
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
It’s very important that you strengthen your pancreas. If there’s a problem with it, start blending the foods listed above in your diet, and make the suggested lifestyle changes. Finally, try out a few of the supplements mentioned above.
A fully functioning pancreas is essential to your good health. Give it some TLC.
Last Updated on September 29, 2022 by Joe Garma