The Interplay of Hormones and Detoxification — Prerequisites for Longevity, Part 3

Hormones and detoxification are two critically important systems that need to be optimized in order to extend healthspan. Like a lot of our physiology, they degrade as we age. Here’s why these systems are important and what you can do to keep them tuned.
Hormones and detoxification are two subjects that you typically don’t see discussed together, but they are interconnected and that relationship is important to understand as we get older. As we age, the intricate symphony of hormones and detoxification processes in our body undergoes changes, impacting our overall well-being and healthspan. Understanding the dynamics between the endocrine system and detoxification phases is crucial for maintaining optimal health in adulthood.
This is Part 3 of a four-part series:
- Part 1 is the Four Exercise Prerequisites of Longevity
- Part 2 is How the Mediterranean Diet Beats the Four Horsemen
- Part 3 you’re reading now
- Part 4 will be about mindset, sleep and intimacy
This post will examine:
- How aging impacts your hormones
- How aging impacts your detoxification system
- Hormones and detoxification are bi-directional
- Hormones and detoxification — how to optimize both
Let’s dig in…
How Aging Impacts Your Hormones
 Hormones are the chemical messengers that govern numerous physiological processes. They are finely regulated by the highly sophisticated and integrated endocrine system. This intricate network of glands, including the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, and reproductive glands, collaborates to produce, release, and modulate the levels of hormones in the body.
Hormones are the chemical messengers that govern numerous physiological processes. They are finely regulated by the highly sophisticated and integrated endocrine system. This intricate network of glands, including the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, and reproductive glands, collaborates to produce, release, and modulate the levels of hormones in the body.
The endocrine system serves as a meticulous conductor, ensuring a delicate balance in hormone concentrations to maintain optimal health and regulate essential functions throughout the body.
What follows is a brief overview of the major hormones affected by the aging process, along with a brief suggestion of countermeasures, which will be addressed more fully later.
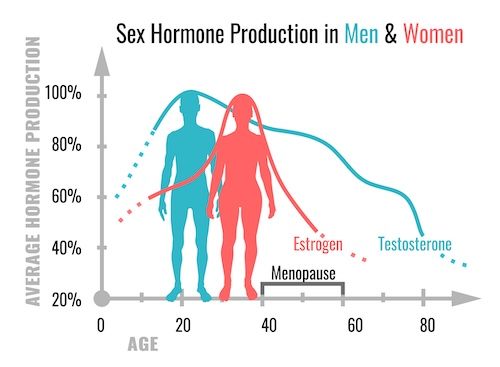
Effects of Declining Estrogen, Progesterone and Testosterone
Estrogen
- Bone Density: Estrogen plays a crucial role in maintaining bone density. As levels decline with age, there’s an increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
- Libido and Vaginal Health: Estrogen influences sexual function and maintains the health of the vaginal tissues. Its reduction may lead to decreased libido and vaginal dryness.
- Menstrual Changes: In women, declining estrogen levels result in irregular menstrual cycles and eventually lead to menopause.
- HRT: To optimize estrogen levels, women can consider hormone replacement therapy (HRT) under the guidance of a healthcare provider
Progesterone
- Estrogen Balance: The steady balance between estrogen and progesterone in a woman’s body undergoes significant changes after menopause: Ovarian function declines, leading to a substantial decrease in the production of both estrogen and progesterone; and there’s an increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures, endometrial hyperplasia or cancer.
- HRT: Balancing progesterone levels through HRT or other hormone optimization therapies may help alleviate symptoms such as irregular periods and mood changes.
Testosterone
- Muscle Mass and Strength: Testosterone contributes to the development and maintenance of muscle mass. Its decline can lead to muscle weakness and decreased physical performance. In men, testosterone levels gradually decrease with age, leading to symptoms like reduced muscle mass and strength.
- Libido: Testosterone is a key factor in maintaining a healthy libido in both men and women.
- Mood and Cognitive Function: Changes in testosterone levels may affect mood, cognitive function, and overall well-being.
- Interventions: Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) may be an option to optimize testosterone levels, but it should be carefully monitored due to potential risks. Both endurance training, or cardio, and strength training may boost your testosterone. Cardio helps you burn fat, while strength training supports the development of lean muscle mass which boosts your metabolism. Of the two types of exercise, strength training has the bigger effect on testosterone levels.
Impact of Decreased Thyroid Function
- Slowed Metabolism: The thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) play a central role in regulating metabolism. Reduced thyroid function can lead to a slowed metabolic rate, potentially resulting in weight gain even with the same dietary habits.
- Fatigue: Hypothyroidism, or decreased thyroid function, is often associated with fatigue and a sense of sluggishness. Insufficient thyroid hormones can impact the body’s ability to generate energy.
- Interventions: Optimizing thyroid hormone levels may involve medication, dietary adjustments, and managing stress.
Effects of Insulin Resistance
- Impaired Glucose Regulation: Insulin resistance occurs when cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin. This leads to elevated blood glucose levels as the body struggles to regulate the uptake of glucose into cells.
- Type 2 Diabetes Risk: Prolonged insulin resistance can progress to type 2 diabetes, a condition where the body cannot use insulin effectively, resulting in chronically elevated blood sugar levels.
- Increased Fat Storage: Insulin resistance is often associated with increased fat storage, particularly around the abdominal area.
- Interventions: To optimize insulin levels, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and following a balanced diet low in added sugars and refined carbohydrates are recommended.
Effects of Cortisol
- The “Stress Hormone”: Cortisol is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands, which are located on top of each kidney. It plays a crucial role in various physiological functions, including metabolism regulation, immune response modulation, and the body’s response to stress. Often referred to as the “stress hormone,” cortisol is released in higher amounts during times of stress to prepare the body for the “fight or flight” response. Additionally, cortisol follows a diurnal rhythm, with levels typically peaking in the early morning and gradually decreasing throughout the day.
- Interventions: Practices such as stress management, mindfulness, and adequate sleep can help optimize cortisol levels and reduce the impact of stress on the body.
It’s important to note that hormone optimization should be approached with caution and under the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider, as it involves individualized assessment and treatment.
Women’s Hormone Replacement Therapy: What You Need to Know
Take This Hormone Questionnaire by Dr. Thierry Hertoghe
My posts about testosterone enhancement
How Aging Impacts Your Detoxification System
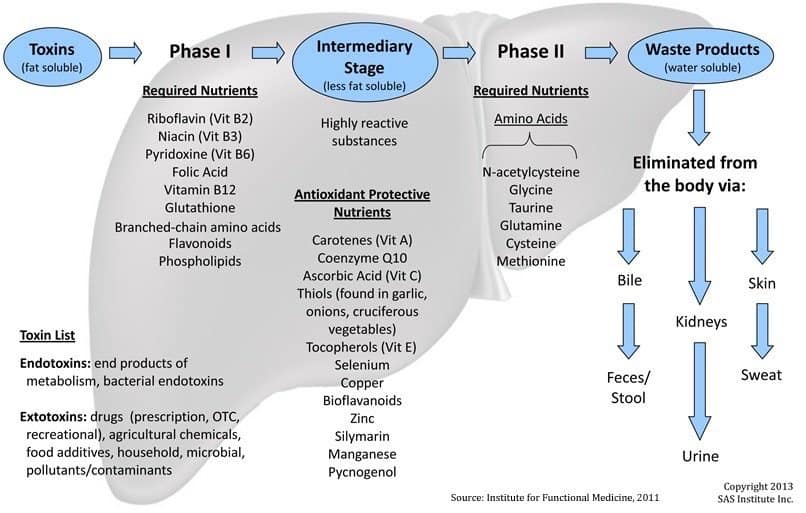
Detoxification is the body’s natural mechanism to eliminate toxins. Divided into three phases, it involves a series of enzymatic reactions, rendering toxins more water-soluble for elimination.
The Three Phases of Detoxification
- Phase I: In this phase, also known as bioactivation or “enzymatic biotransformation”, the liver primarily transforms lipid-soluble toxins into less harmful intermediate products. This transformation is essential for the subsequent phases of detoxification.
- Phase II: Enzymatic conjugation is the key process in this phase, where the now-reactive intermediate products from Phase I are further processed to become water-soluble and ready for excretion. From the perspective of biology, to “conjugate” is to become temporarily united in order to exchange genetic material.This phase involves the addition of water-soluble groups to the reactive sites created in Phase I.
- Phase III: Transport, The Antiporter System is a crucial step in completing the detoxification process, whereby the water-soluble, conjugated toxins are transported out of the cells so that they can be excreted from the body via feces, urine and sweat.
These phases work together to protect and heal the body by identifying, transforming, and eliminating toxins. Supporting each phase individually can enhance their synergistic activity, contributing to overall detoxification and health.
You may read more about these phases of detoxification in my post, Why You Must Detox All The Time, Part 3/3: How To Make Your Detox Pathways Work.
Why Detoxification Is Necessary
We live in a toxic world. We are constantly ingesting, inhaling and absorbing toxins that will make us sick if not properly detoxified and excreted. I’ll quickly prove my point and then suggest you read my post, Our World Is Toxic and So Are We, if you’d like more details about our toxin burden.
Common toxins that the body needs to detoxify include [5][6][7]:
- Pollutants and Synthetic Chemicals: These can be found in the air, water, and food, and include substances like pesticides, heavy metals, and industrial chemicals .
- Processed Foods: Certain food additives, preservatives, and artificial ingredients present in processed foods may be considered toxins that the body needs to eliminate.
- Heavy Metals: Substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium can be toxic to the body and are typically eliminated through the detoxification process.
- Waste Products: Metabolic byproducts and waste substances produced within the body, such as urea and carbon dioxide, are also considered toxins that need to be excreted.
- Pollutants and Synthetic Chemicals: These can be found in the air, water, and food, and include substances like pesticides, heavy metals, and industrial chemicals.
- Processed Foods: Certain food additives, preservatives, and artificial ingredients present in processed foods may be considered toxins that the body needs to eliminate.
- Heavy Metals: Substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium can be toxic to the body and are typically eliminated through the detoxification process.
- Waste Products: Metabolic byproducts and waste substances produced within the body, such as urea and carbon dioxide, are also considered toxins that need to be excreted.
As we covered above, it’s important to note that the body has its own built-in mechanisms (the three phases of detoxification) to eliminate these toxins, primarily through organs like the liver, kidneys, skin and lungs. While various products and diets claim to aid in detoxification, the body’s natural detoxification processes are generally effective at removing harmful substances without the need for special interventions — unless your toxic burden gets so “heavy” that it overwhelms your endogenous detox system.
Unfortunately, the aging process can impact each detoxification phase, potentially leading to a decreased ability to eliminate toxins efficiently.
How Aging Impacts Detoxification
As individuals age, the efficiency of the body’s natural detoxification processes may decline, potentially leading to a reduced ability to eliminate toxins. This decline can be attributed to various factors, including changes in enzyme activity, nutrient status, and overall physiological function. Additionally, the accumulation of toxins over time can further burden the body’s detoxification systems, potentially leading to an increased risk of toxin-related health issues [8].
The aging process can inhibit the body’s ability to detoxify toxins related to the phases of detoxification that I introduced above. Such pathways are highly dependent on proper nutrient support for optimal functioning, and the aging process can affect their efficiency 4 For instance, detoxification mechanisms, including the removal of electrophiles by glutathione transferase-catalyzed conjugation, are major longevity assurance mechanisms and can be impacted by the aging process [9][10].
Additionally, the accumulation of toxins over time can further burden the body’s detoxification systems, potentially leading to an increased risk of toxin-related health issues.
Some common toxins that the body may struggle to detoxify in older adults include:
- Pesticides and Herbicides: Daily exposure to environmental toxins like pesticides and herbicides can challenge the body’s natural detoxification processes, particularly as individuals age [11].
- Plastics: Toxins from plastics, such as bisphenol A (BPA), can pose challenges to the body’s detoxification systems, especially as individuals grow older [11].
Heavy Metals: Accumulation of heavy metals like lead, mercury, and cadmium over time can strain the body’s ability to eliminate these toxins, particularly in older adults [12]. - Electrophiles: Aging-related toxicants, including electrophiles, can impact the body’s detoxification systems, such as glutathione transferase-catalyzed conjugation, which are major longevity assurance mechanisms [13][14].
These toxins can present challenges to the body’s natural detoxification processes, especially as individuals age, and may require additional support to maintain overall health and well-being.
Hormones and Detoxification are Bi-directional
Understanding and adjusting your lifestyle to the interplay between hormones and detoxification is crucial for maintaining overall health, especially as we age. By adopting a holistic approach that encompasses nutrition, lifestyle, and environmental factors, we can support our body’s natural ability to balance hormones and eliminate toxins.
What you’ve learned so far is that the endocrine system is a complex network of glands and organs that produce and regulate hormones, which are chemical messengers that control various bodily functions. As we age, the production and balance of hormones can be impacted, leading to symptoms such as irregular periods, weight gain, and fatigue [15][16].
On the other hand, detoxification is the process of eliminating toxins from the body, typically occurring in four phases. As you’ve learned, these phases involve various biochemical reactions that transform toxins into less harmful substances that then are excreted. You also learned that the aging process can affect both the endocrine system and the detoxification phases. For instance, as we age, the efficiency of the liver, which is a key organ in detoxification, may decrease, leading to a reduced ability to eliminate toxins from the body [17]. Similarly, the production of certain hormones may decline with age, impacting various bodily functions [15].
What I want to impress upon you now is that the relationship between hormones and detoxification is bidirectional: Hormonal imbalances can  affect the body’s ability to detoxify, and conversely, a high toxic burden can lead to hormonal imbalances
affect the body’s ability to detoxify, and conversely, a high toxic burden can lead to hormonal imbalances
Here are a few examples:
- Estrogen and Detoxification: Estrogen metabolism is closely linked to detoxification processes. Changes in estrogen levels can influence the efficiency of detoxification pathways, potentially impacting the body’s ability to eliminate toxins [18][19].
- Thyroid Hormones and Detoxification: Thyroid hormones also play a role in the regulation of detoxification enzymes. Reduced thyroid function may contribute to a sluggish detoxification process [20].
- Insulin and Detoxification: Insulin resistance and associated metabolic disturbances can affect the body’s ability to handle toxins, potentially contributing to a higher toxic burden [21][22].
These are among the most pernicious toxins that can disrupt endocrine function and hormonal balance:
- Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs): These are substances in the environment, food sources, personal care products, and manufactured products that interfere with the normal function of the body’s endocrine system. EDCs can act like “hormone mimics,” block natural hormones from doing their job, or` change how sensitive the body is to different hormones. They have been linked to adverse human health outcomes, including alterations in sex organs, endometriosis, early puberty, altered nervous system function, immune function, certain cancers, respiratory problems, metabolic issues, diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular abnormalities [23].
- Phytoestrogens: These are natural chemicals found in human and animal food, such as genistein and coumestrol. They can act as endocrine disruptors by interfering with hormone biosynthesis, metabolism, or action, resulting in a deviation from normal homeostatic control or reproduction [24]
- Bisphenol A (BPA): Found in many everyday products, including some plastics and food packaging. BPA can mimic estrogen and interfere with the endocrine system, potentially leading to hormonal imbalances [25].
- Phthalates: These are a group of chemicals used to make plastics more flexible and harder to break. They are often found in products such as vinyl flooring, adhesives, detergents, lubricating oils, automotive plastics, plastic clothes (raincoats), and personal-care products (soaps, shampoos, hair sprays, and nail polishes). Phthalates can disrupt the endocrine system by interfering with hormone biosynthesis, metabolism, or action [26].
To support hormone balance and detoxification, individuals can take several steps. These include consuming foods that support liver function and hormone metabolism, such as cruciferous vegetables and probiotic-rich foods [27][28].
Additionally, lifestyle factors like stress management, regular exercise, and reducing toxin exposure can also contribute to maintaining hormone balance and supporting the body’s detoxification processes [29][30].
Hormones and Detoxification — How to Optimize Both
At this point, you know about the impact that aging and toxins have upon your endocrine system (hormones) and detoxification mechanisms. Now, let’s address what you can do about it through the lens of lifestyle factors and supplementation.
Lifestyle Factors that Can Improve Hormonal Balance and Detoxification
Some natural ways to balance hormones and support detoxification include:
- Improving Gut Health: A healthy gut is essential for hormone balance and effective detoxification. Consuming probiotic-rich foods and adding probiotic supplements can support digestive bacteria and aid in hormone detox [31].
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Chronic inflammation can disrupt hormone production. An anti-inflammatory diet, rich in whole foods and low in processed items, can help balance hormones and support the body’s natural detoxification processes [32][33]. This includes the consumption of healthy fats, such as omega-3-fatty acids found in walnuts, avocado, chia, flax and hemp seeds [34].
- Detoxification Programs: Engaging in a well-designed detox program can help remove toxins from the body, enhance the body’s natural detoxification abilities, and improve the body’s ability to make and use hormones. This involves replacing processed foods with whole foods, increasing water intake, and using supplements to support the body [32].
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve hormone levels, burn off excess stress hormones, and help eliminate toxins from the body through perspiration [35][36].
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough quality sleep is crucial for hormone balance and effective detoxification. It supports the body’s natural repair and regeneration processes, including the elimination of toxins [35][36].
- Stress Management: Practices such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help reduce stress hormones, support hormone balance, and aid in the body’s detoxification efforts[35][36].
- Use of Natural Cleaning Products: Limiting the use of commercial cleaning products that contain harsh chemicals, and opting for natural alternatives to reduce toxin exposure [37].
- Hydration: Drinking an adequate amount of water to support the body’s natural detoxification processes, such as kidney function and toxin elimination through urine [38][39].
- Stress Management: Practicing stress-reducing activities such as mindfulness, meditation, and adequate sleep to support the body’s ability to eliminate toxins [40].
Supplements that Can Improve Hormonal Balance and Detoxification
Notwithstanding that the most effective way to improve hormonal secretions is through HRT, the following supplements can help given that they support detoxification:
- Glutathione and N-acetylcysteine (NAC): These supplements play crucial roles in detoxification. Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that helps remove toxins from the body, such as mercury, and supports immune, respiratory, brain, and liver health. It also regenerates other antioxidants like vitamins C and E. NAC stimulates glutathione biosynthesis, promotes detoxification, and acts directly as a scavenger of free radicals. It’s a powerful antioxidant and a potential treatment option for diseases characterized by oxidative stress. NAC also plays a role in the detoxification of the kidneys and liver, and it helps to prevent potential side effects of drugs and environmental factors [41][42][43][44][45].
- Milk Thistle: Known for its liver-protective properties, it is a powerful antioxidant that supports the liver in eliminating toxins [46][47].
- Dandelion Root: This herb supports liver function and digestion, aiding in the detoxification process
- [46][47].
- Ginger: It has anti-inflammatory properties and can help with digestion, potentially supporting the body’s natural detox processes [46].
- Turmeric: A potent antioxidant with anti-inflammatory properties, it can aid in reducing inflammation and supporting overall detoxification [47].
- Vitamins and Minerals: Certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium, act as antioxidants and support the body’s natural detox processes [48][49].
- Probiotics: These beneficial bacteria support gut health, which is crucial for effective detoxification and overall well-being [50].
Go to:
Last Updated on February 7, 2024 by Joe Garma