Discover Your Biological Age With These 4 Tests, Part 3: Epigenetic Age

Epigenetic age is the age your are biologically. By calendar years, you may be 50 years old, but your epigenetic age might be ten years, or any number of years, younger or older. Your epigenetic age is the only number that matters, because that’s how old (or young) you really are.
Epigenetic age, and how to test it, is the focus on this final piece in a three-part series about how to test your biological age.
For context, the four biological age tests covered in this three-part series are:
- Survey-based (Part 1)– Evaluates your answers to questions about lifestyle factors thought to impact aging
- Physical/Emotional Tests (Part 1) — Assesses responses to physical and emotional outputs
- PhenoAge Test (Part 2)– Quantifies bioage using utilizing nine blood biomarkers
- Methylation Tests (here in Part 3)– Measures patterns of methyl groups on DNA associated with gene expression
Here's what we're going to cover in this post:
Let’s dive in..
What Is Epigenetics and Why It Matters to You?
Epigenetics” means “above genetics”, and as such epigenetics the study of:
“… heritable changes in gene expression or cellular phenotype caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence.” (Source)
That’s a mouthful.
We need an example. Let’s use computer hardware (the machine) and software (instructions to the machine) to get a better sense of what epigenetics is about. Although this isn’t always true, in this instance the genome (all our DNA) represents the computer hardware (our body) that is distinct from the epigenome, the software that tells the body what to do.
The hardware DNA will stay the same throughout your life, but the epigenetic “tags” do change, and they decide what genes get expressed, just as one computer can have many different types of software that will make it do different things.
These tags are largely determined by your environment, such as how much air pollution you breathe or toxins your exposed to, and behavior, such as your diet, stress level and physical activity, or lack thereof.
And all this is why a common refrain in the field of epigenetics is:
“Genetics loads the gun, but behavior pulls the trigger.”
What we do, eat, smoke, our stress level — they all affect what genes get triggered, as I’ll describe later. But first, more about these “tags”.
DNA, Methylation and Histones
DNA is a molecule composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double 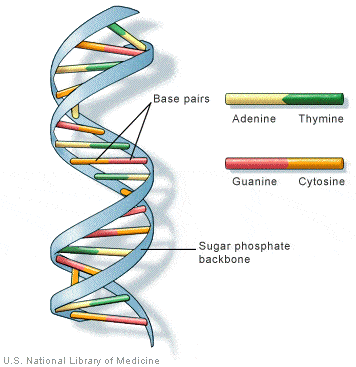 helix carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.
helix carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.
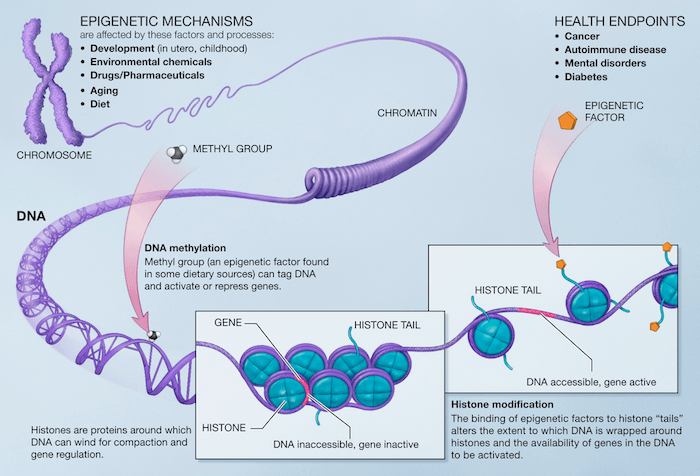
The epigenome is a set of chemical modifications attached to DNA that affects how the genes are expressed. There are two types of chemical tags:
- DNA methylation – this directly affects the DNA in a genome, as chemical tags called methyl groups, or methyls, are attached to individual DNA bases in specific places. The methyl groups are attached by proteins and switch genes on or off by adjusting interactions between the DNA and other proteins. These tags mean that cells can keep track of which genes are on or off.
- Histone modification – affects DNA indirectly. DNA is a long string of information, so to keep it tidy and prevent damage, cellular DNA is wrapped around histone proteins; this forms a neatly wound-up package, rather like a spool. Just like on DNA, proteins can attach various chemical tags to the histones which can be detected by other proteins in cells, which then determine whether that region of DNA should be read or ignored in that particular cell.
The image below nicely illustrates how DNA is affected by DNA methylation and histone modification. The chromosome, which is made up of DNA, is unraveled to chow how methyl chemicals can tag DNA and thereby activate or repress genes. Histones are the proteins that compress the DNA by winding them up in a spool, a process that further affects the availability of the genes in the DNA to be activated.
Is Your Epigenome Fixed?
Although your DNA is fixed and unalterable, given the current state of science, your epigenome is constantly changing; alterations to it occur throughout your life. Beginning at conception, DNA methylation and rearrangement of histones happens as cells become specialized (lung vs kidney cells). The intrauterine environment to which a fetus is exposed causes methylation, and as we are born and life our life, the lifestyle choices we make (diet, exercise) and various environmental factors (water and air quality) will affect the epigenome, and thereby our healthspan, for better or worse.
Thus, should you desire to live a long and healthy life, the reason your epigenome matters to you is because you’re in the drivers seat — what you do or don’t do matters.
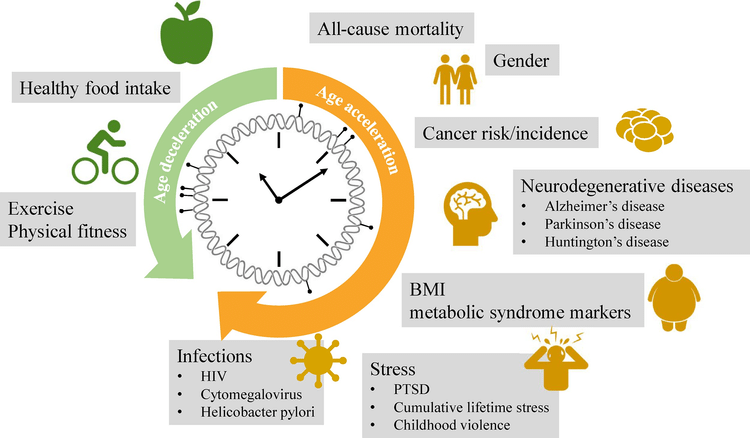
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors Impact Your Epigenetic Age
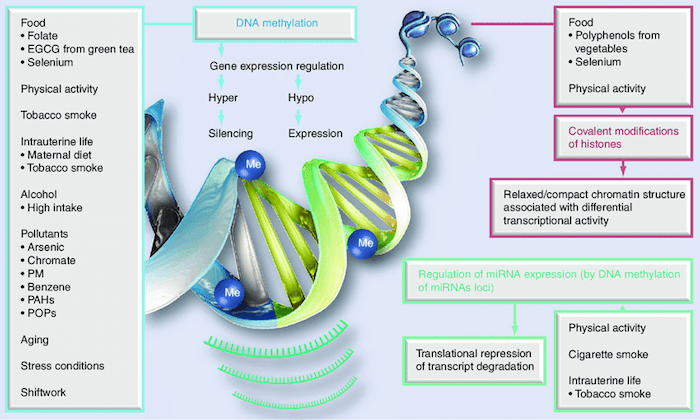
Credit: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lifestyle-factors-participating-in-environment-epigenetic-interactions-EGCG_fig1_51831633
Epigenetic changes can be triggered by many things, and they pretty much all can be regarded as lifestyle and environmental factors, which going forward I’ll refer to as “lifestyle factors”.
Life throws many challenges at us, as do the decisions we make about where to live, what to eat, how much sleep to get and many more conscious and unconscious choices we make that affect our epigenetic age, because in response to these challenges and decisions, the epigenome alters our DNA expression to be altered in response.
Various lifestyle and environmental factors (smoking, diet, infection, exposure to sunlight or pollution) can apply biological pressure that prompt chemical responses and result in methylation. DNA methylation is strongly correlated with aging, and if it causes malfunctions in protein expression, can lead to various diseases.
Lifestyle factors associated with slowed epigenetic aging include:
- Higher fish intake
- Higher carotenoid levels (a marker of fruit and vegetable intake)
- Higher education
- Moderate alcohol consumption
- Higher physical activity
- Higher HDL (“good” cholesterol)
Lifestyle factors associated with accelerated epigenetic aging include:
- Higher BMI
- Higher LDL (“bad” cholesterol)
- Higher triglycerides
- Higher blood pressure
- Metabolic syndrome (associated with all of the above)
So, there’s good news and bad news when it comes to healthspan and epigenetic age:
- The good news — your biological age is in your hands.
- The bad news — your biological age is in your hands.
If you need some ideas and inspiration, check these out:
Remember: Your DNA is fixed, but how your genes are expressed (turned “on” and “off”) is largely up to you. Which brings us to the last part of this piece — how to measure your epigenetic age.
Three Epigenetic Age Tests
Epigenetic age can be accurately estimated by changes in DNA methylation. There are several companies that offer at-home epigenetic age tests that do that, typically via saliva or urine samples. I hopped around the Interwebs and found no quantitative comparisons among these tests, so I will show you three that have been conceived by reputable scientists and offered by reputable companies:
- Index by Elysium Health
- TruAge by TruDiagnostic
- myDNAge by myDNA
Unfortunately, I cannot assess which test does the better job of determining epigenetic age. Don’t let price be your only decision metric — the most expensive aren’t necessarily better, and the least expensive isn’t necessarily a better deal.
#1 Index by Elysium Health – $499 
Index was developed by Elysium Health in concert with and licensed from gerontologist Dr. Morgan Levine, who with Dr. Steve Horvath developed the PhenoAge test described in Part 2.
Index tracks how fast you’ve been aging using the latest epigenetics technology. Index offers:
- Biological Age, a measure of the average age at which your body is expected to function
- Cumulative Rate of Aging, the pace at which your body has aged for every year you’ve been alive
- Science-backed lifestyle recommendations you can use to adopt healthier habits
Index uses an algorithmic platform for epigenetic examination (APEX) that calculates your biological age by examining more than 100,000 sites on your DNA where methylation has taken place.
Elysium claims that their computational approach significantly improves upon past biological clocks, because it’s:
- The most precise epigenetic biological age test
- Has equivalent or better predictive powers than the PhenoAge test (see Part 2 for PhenAge info.)
- Is better at tracking lifestyle changes over time than other tests
#2 TruAge by TruDiagnostic — $499 
TruDiagnostic is a company that specializes in epigenetic testing and research. The TruAge epigenetic age test uses a variety of algorithms, one licensed from Duke University that analyses complex patterns of DNA methylation to detect just how fast a person is aging when tested.
#3 myDNAge by myDNA — $299 
myDNA offers both a blood and urine test, both taken at-home.
The myDNAge® Test is an epigenetic age determination test. This biological age test is based on Dr. Steve Horvath’s epigenetic aging clock and utilizes our proprietary SWARM™ (Simplified Whole-panel Amplification Reaction Method) technology to analyze DNA methylation patterns of over 2,000 loci on the human genome and generate epigenetic age predictions in a high throughput manner.
I have yet to take any of these tests. Given that my annual health check up includes the nine blood tests required to calculate the very accurate PhenoAge test, I rely on that, in part, to monitor my biological age. For more on that, go here.
Your Epigenetic Age Takeaway
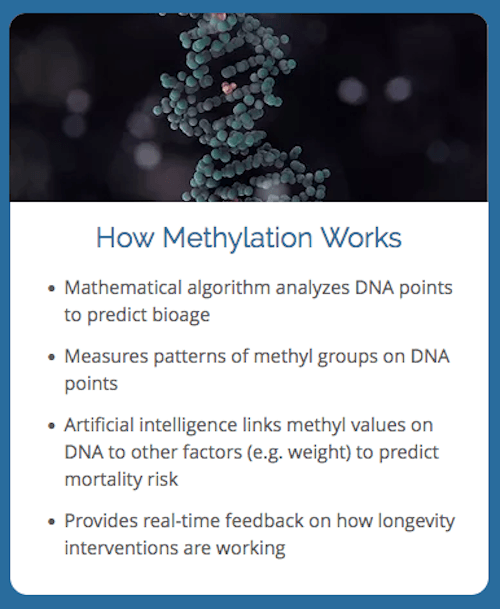
First, remember how methylation epigenetic age testing works:
Next, remember these three things:
- Genetics loads the gun, but behavior pulls the trigger. This adage refers to the fact that your lifestyle choices (your behavior) influences how your genes are expressed through epigenetics, so choose wisely the various lifestyle factors covered here that can make you biologically younger.
- Three epigenetically influential things you can do is to: (1) Eat more fish, veggies and fruit; (2) Exercise regularly; (3) Get plenty of restful sleep; (4) Reduce stress; (5) Get rid of belly fat.
- You can test your epigenetic age at home. The three tests covered here are:
Last Updated on November 22, 2021 by Joe Garma